300+ project management templates & documents in Excel at: https://lnkd.in/gJkgsbn
Use Project Management Templates to Reduce Effort and Increase your productivity
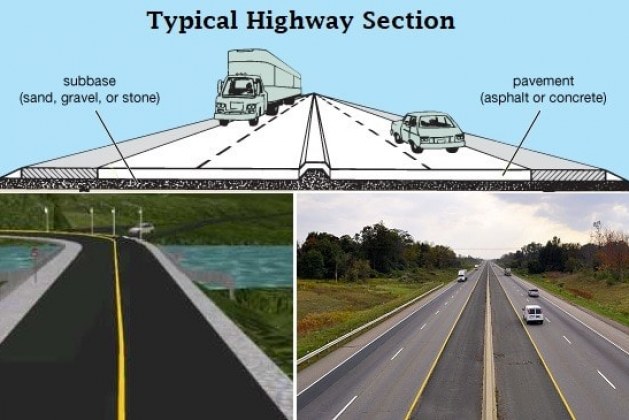
Highway geometric design in which representative sample (cross-section) element, view (sight) length (distance) concept, and horizontal & vertical arrangement are assumed to be set. Pavement attributes:
- Longitudinal friction is equal to .35 to .4
- Lateral friction is equal to .15
- The highway must not be light reflecting in day, but light reflecting in night.
- Permitted differences or unevenness must not be more than 150 cm/km
Representative sample (Cross-sectional or cross-section) Part The highway is parted into 2: the pavement and curb stone. The pavement possesses a gradient which is called camber. The gradient or slope is for draining purposes. The gradient is offered in respect of θ and computed in respect of n. Camber = 1/n percent or tan θ The camber is of 2 sorts. The initial one is triangulated camber and the subsequent is parabolic camber.
Triangulated camber can be computed like y = w/2n Parabolic camber is y = 2x2/wn ‘y’ is the camber height, ‘w’ is the pavement width, and ‘x’ is the length or distance from the periphery (side). Gradient = 2(camber)
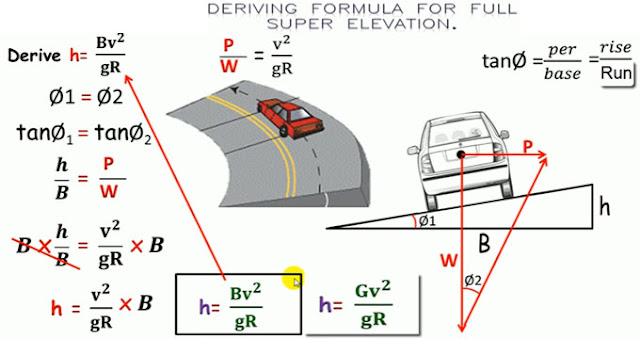
When a road becomes an upright turn, the upright height is called θ, which is an incline, and the horizontal incline (indicates the camber) which is offered as θ. It’s called the camber.
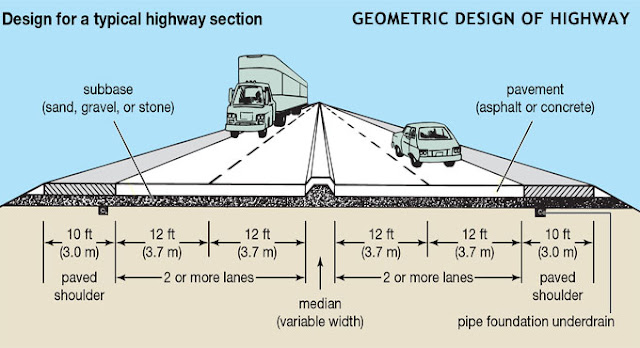
Carriage way or Pavement width arrangement: The overall dimension (length) in which a major vital highway is built is called formation width (which is 12 m). It comprises 2 pavements, 1 median wherein the planting is performed and 2 shoulders by the pavements parts.
- At 45 m on the two sides, there’ll be a road periphery.
- At 80 m, there’ll be a structure periphery. 150 m is control line.
- The 150 m control line is called Right of way.
- Pavement width For a Single lane – 3.75 m For 2 lane without kerb – 7.0 m
- For 2 lanes with kerb – 7.5 m Intermediate lanes are set as 5.5 m
- For Multilane – 3.5 m for every lane
To get detail information on geometric design for highway engineering, go through the following video tutorial.
https://youtu.be/cnfp5ixnTUQ